Antentop is FREE e-magazine devoted to Antennas and Amateur Radio an
Special page devoted to
Vacuum Tubes

Custom Search
|
ANTENTOP-
03- 2003, # 004
|
Vacuum Tubes
|
||
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
Historical notes about
development of tubes from early years to our days in the World
and in Russia |
Vitaly Brousnikin, vitalybr@onego.ru http://oldradio.onego.ru/ |
||
|
For a time receiving and amplifying
valves were named in this country "cathode" or "vacuum
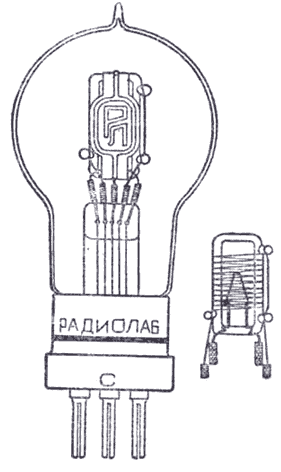
relay". The first Russian mass valve designed in 1918 at
the Radio Laboratory of the town of Nizhny Novgorod under supervision
of M.A.Bonch-Brouyevich (on the basis of the first model - "Babushka"
tube) was named PR-1 ("vacuum
relay, model no.1"). The name of the R-5
valve produced in 1922 by the Petrograd Electro-Vacuum Works meant:
"relay, model no.5. A new valve with thoriated cathode produced
in 1923 consuming a ten times less |
PR-1 |
||
|
1. R5 2. Micro 3. MDS |
denomination. A 'letter
and figure' system of marking was introduced, which remained till
early 1940's. The first letter in the valve marking shows |
||
|
heating
current than the "R-5",
was named the "Micro".
Equally economical of heating
a two-grid valve with "cathode grid" was named "MDS" ("micro, two-grid").The
first low-powered vacuum rectifier was |
it's
category: "P" - receiving, "U" - amplifying,
"S" - special, "V" - rectifying, "T"
- broadcasting, "N" - low-frequency. The second letter
described the cathode - "T" - thoriated, "K"
- carbonized, "B" - bariated, "O" - oxide.
The figure included |
||
|
|
|
||
|
Page 92 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
Just for Fun:

Powered byIP2Location.com
Thanks for your time!
Last Updated:
February 29, 2020 23:03